This Vitamin Deficiency Is A Silent Epidemic with Serious Consequences (Video)
by N.Morgan

If you have a vitamin B12 deficiency, you could become anemic. A mild deficiency may cause no symptoms. But if untreated, it may lead to symptoms such as weakness, tiredness, or lightheadedness. Heart palpitations and shortness of breath.
What do all of these chronic diseases have in common?
- Alzheimer’s, dementia, cognitive decline, and memory loss (collectively referred to as “aging”)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) and other neurological disorders
- Mental illnesses like depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and psychosis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Learning or developmental disorders in kids
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Autoimmune disease and immune dysregulation
- Cancer
- Male and female infertility
Answer: They can all mimic the signs and symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency.
An Invisible Epidemic
B12 deficiency isn’t a bizarre, mysterious disease. It’s written about in every medical textbook, and its causes and effects are well-established in the scientific literature.
However, the condition is far more common than most healthcare practitioners and the general public realize. Data from a Tufts University study suggests that 40 percent of people between the ages of 26 and 83 have plasma B12 levels in the low normal range—a range at which many experience neurological symptoms. Nine percent had an outright nutrient deficiency, and 16 percent exhibited “near deficiency.” Most surprising to the researchers was the fact that low B12 levels were as common in younger people as they were in the elderly. (1)
That said, this type of deficiency has been estimated to affect about 40 percent of people over 60 years of age. It’s entirely possible that at least some of the symptoms we attribute to “normal” aging—such as memory loss, cognitive decline, and decreased mobility—are at least in part caused by a deficiency.

Why Is It Underdiagnosed?
B12 deficiency is significantly underdiagnosed for two reasons. First, it’s not routinely tested by most physicians. Second, the low end of the laboratory reference range is too low. This is why most studies underestimate true levels of deficiency. Many deficient people have so-called “normal” levels of B12.
Yet, it is well-established in the scientific literature that people with B12 levels between 200 pg/mL and 350 pg/mL—levels considered “normal” in the U.S.—have clear vitamin deficiency symptoms. (2) Experts who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of a deficiency, like Sally Pacholok, R.N., and Jeffrey Stuart, D.O., suggest treating all patients that are symptomatic and have B12 levels less than 450 pg/mL. (3) They also recommend treating patients who show normal B12 levels but also have elevated urinary methylmalonic acid (MMA), homocysteine, or holotranscobalamin, which are other markers of a deficiency in vitamin B12.
B12 deficiency can mimic the signs of Alzheimer’s, dementia, multiple sclerosis, and several mental illnesses. Find out what this vitamin does and learn how to treat a deficiency.
In Japan and Europe, the lower limit for B12 is between 500 and 550 pg/mL. Those levels are associated with psychological and behavioral symptoms, such as:
- Cognitive decline
- Dementia
- Memory loss (4)
Some experts have speculated that the acceptance of higher levels as normal in Japan and the willingness to treat levels considered “normal” in the U.S. explain the low rates of Alzheimer’s and dementia in that country.
What Is Vitamin B12 and Why Do You Need It?
Vitamin B12 works together with folate in the synthesis of DNA and red blood cells. It’s also involved in the production of the myelin sheath around the nerves and the conduction of nerve impulses. You can think of the brain and the nervous system as a big tangle of wires. Myelin is the insulation that protects those wires and helps them to conduct messages.
Severe B12 deficiency in conditions like pernicious anemia (an autoimmune condition where the body destroys intrinsic factor, a protein necessary for the absorption of the vitamin) used to be fatal until scientists figured out death could be prevented by feeding patients raw liver, which contains high amounts of B12. But anemia is the final stage of a deficiency. Long before anemia sets in, deficient patients will experience several other problems, including fatigue, lethargy, weakness, memory loss, and neurological and psychiatric problems.
The Stages of a Deficiency
B12 deficiency occurs in four stages, beginning with declining blood levels of the vitamin (stage I), progressing to low cellular concentrations of the vitamin (stage II), an increased blood level of homocysteine and a decreased rate of DNA synthesis (stage III), and finally, macrocytic anemia (stage IV). (5)
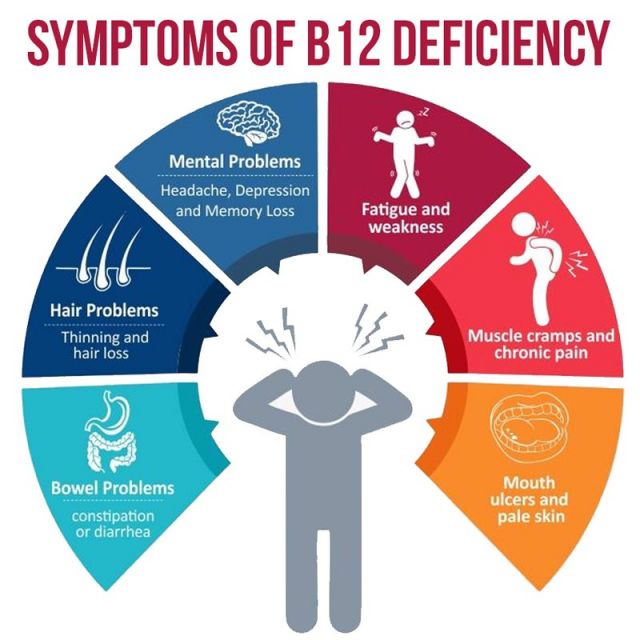
Common B12 Deficiency Symptoms
The signs can look like the symptoms of several other serious disorders, and the neurological effects of low B12 can be especially troubling.
Here are some of the most common vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms:
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Brain fog, confusion, and memory problems
- Depression
- Premature aging
- Cognitive decline
- Anemia
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
- Constipation
- Trouble balancing (6)
Children can also show symptoms, including developmental issues and learning disabilities if their B12 levels are too low.
Why Is It So Common?
The absorption of B12 is complex and involves several steps—any of which can go wrong. Any of the following can cause B12 malabsorption:
- Intestinal dysbiosis
- Leaky gut and gut inflammation
- Atrophic gastritis or hypochlorhydria, or low stomach acid
- Pernicious anemia
- Medications, especially proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and other acid-suppressing drugs
- Alcohol
- Exposure to nitrous oxide, during either surgery or recreational use
This explains why a deficiency can occur even in people eating large amounts of B12-containing animal products. In fact, many of my patients that are B12 deficient are following a Paleo diet where they eat meat two or three times daily.
Who Is at Risk for a Deficiency?
In general, the following groups are at greatest risk for a deficiency:
- Vegetarians and vegans
- People aged 60 or over
- People who regularly use PPIs or acid-suppressing drugs
- People on diabetes drugs like metformin
- People with Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac, or IBS
- Women with a history of infertility and miscarriage
Note to Vegetarians and Vegans: B12 Is Found Only in Animal Products
You cannot get B12 from plant-based sources. This vitamin is only found in animal products. That’s why vegetarians and vegans need to know the signs of deficiency—and the steps necessary to fix the problem.
B12 is the only vitamin that contains a trace element (cobalt), which is why it’s called cobalamin. Cobalamin is produced in the gut of animals. It’s the only vitamin we can’t obtain from plants or sunlight. Plants don’t need B12, so they don’t store it.
A common myth among vegetarians and vegans is that it’s possible to get B12 from plant sources like:
- Seaweed
- Fermented soy
- Spirulina
- Brewers yeast
However, plant foods said to contain B12 actually contain B12 analogs called carbamides that block the intake of and increase the need for true B12. (7) That explains why studies consistently demonstrate that up to 50 percent of long-term vegetarians and 80 percent of vegans are deficient in B12. (8, 9)
The Impact of a Deficiency on Children
The effects of B12 deficiency on kids are especially alarming. Studies have shown that kids raised until age six on a vegan diet are still B12 deficient even years after they start eating at least some animal products. In one study, the researchers found an association between a child’s B12 status and their performance on testing measuring:
- Spatial ability
- Fluid intelligence
- Short-term memory
Researchers found that formerly vegan children scored lower than their omnivorous counterparts in each area. (10)
The deficit in fluid intelligence is particularly troubling, the researchers said, because this area impacts a child’s ability to reason, work through complex problems, learn, and engage in abstract thinking. Defects in any of these areas could have long-term consequences for kids.
I recognize that there are many reasons why people choose to eat the way they do, and I respect people’s right to make their own choices. I also know that, like all parents, vegetarians and vegans want the best for their children. This is why it’s absolutely crucial for those that abstain from animal products to understand that there are no plant sources of B12 and that all vegans and most vegetarians should supplement with B12.
This is especially important for vegetarian or vegan children or pregnant women, whose need for B12 is even greater. If you’re not willing to take a dietary supplement, it may be time to think twice about your vegetarian or vegan diet.
How to Treat a Deficiency
One of the greatest tragedies of the B12 epidemic is that diagnosis and treatment are relatively easy and cheap—especially when compared to the treatment patients will need if they’re in a late stage of deficiency. A B12 test can be performed by any laboratory, and it should be covered by insurance. If you don’t have insurance, you can order it yourself from a lab like DirectLabs.com.
As always, adequate treatment depends on the underlying mechanism causing the problem. People with pernicious anemia or inflammatory gut disorders like Crohn’s disease are likely to have impaired absorption for their entire lives and will likely require B12 injections indefinitely. This may also be true for those with a severe deficiency that’s causing neurological symptoms.
Some recent studies have suggested that high-dose oral or nasal administration may be as effective as injections for those with B12 malabsorption problems. (11) However, most B12 experts still recommend injections for people with pernicious anemia and an advanced deficiency involving neurological symptoms.
Try Supplementing
Cyanocobalamin is the most frequently used form of B12 supplementation in the U.S. But recent evidence suggests that hydroxocobalamin (frequently used in Europe) is superior to cyanocobalamin, and methylcobalamin may be superior to both—especially for neurological disease.
Japanese studies indicate that methylcobalamin is even more effective in treating neurological symptoms and that it may be better absorbed because it bypasses several potential problems in the B12 absorption cycle. (12, 13) On top of that, methylcobalamin provides the body with methyl groups that play a role in various biological processes important to overall health.

Change Your Diet
Nourishing your body through whole food is the best way to get the vitamins and nutrients you need. If you’re low on B12, try eating some vitamin-rich foods like:
- Liver
- Shellfish
- Clams
- Oysters
- Organ Meats
Eating other kinds of seafood, like an octopus, fish eggs, lobster, and crab, can also help you attain normal B12 levels. If you’re seafood-averse, you can also get this vitamin from:
- Lamb
- Beef
- Eggs
- Cheese
It’s important to note, though, that the amount of B12 in these foods is nowhere near as high as the levels in shellfish and organ meats.
What to Do if You’re Experiencing Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms
If you suspect you have a deficiency, the first step is to get tested. You need an accurate baseline to work from.
If you are B12 deficient, the next step is to identify the mechanism causing the deficiency. You’ll probably need help from a medical practitioner for this part. Once the mechanism is identified, the appropriate form (injection, oral, sublingual, or nasal) of supplementation, the dose, and the length of treatment can be selected.
So, next time you or someone you know is “having a senior moment,” remember: It might not be “just aging.” It could be B12 deficiency.
We have an affiliate program designed for content creators and affiliate marketers, who would like to sell this product, please click here for affiliate program details. Our affiliate program is designed to help you monetize your screen time.

References:

.png)

.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment